about us
News Center
Your current location:Home - About us - News center
Charge is the
inherent property of matter. Usually, the number of positive and negative
charges in an object is equal. Once an object loses or gains some electrons, it
will show negative or positive charges. A regular motion of the charge produces
an electric current.
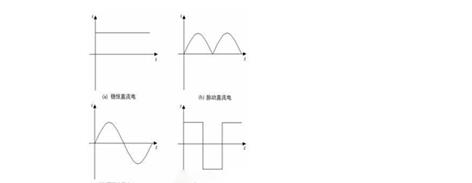
1. DC: If in a
circuit, the charge flows in a constant direction, this is "DC". In
daily life, the current provided by the "battery" is the direct
current. Batteries have polarity, which can be divided into
positive and
negative electrodes.
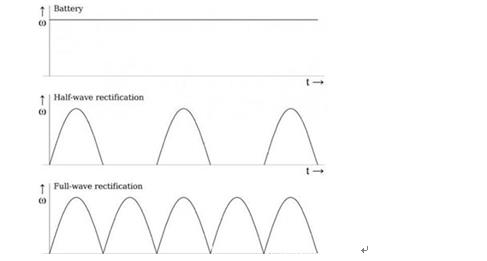
2. AC: When the
current in the circuit changes periodically with the direction and intensity,
it is called "AC". Electric energy produced by modern power plants is
alternating current, so are household and industrial power.
Difference between
DC and AC
The alternating
current varies according to the sinusoidal curve and has its frequency; the
direct current does not change according to the sinusoidal curve and has no
frequency change. The most intuitive difference between alternating current and
direct current is that the direction of the current is unchanged; the direction
of the current of direct current is unchanged at any time, but the size may
change; the most special direct current is the steady current whose direction
is unchanged. The so-called alternating current is the alternating flow of
current, its direction is alternating change.
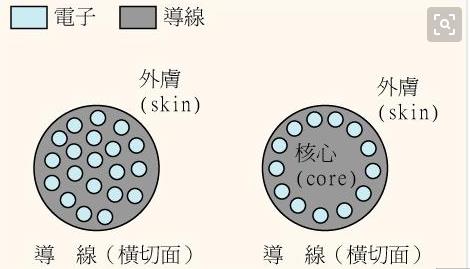
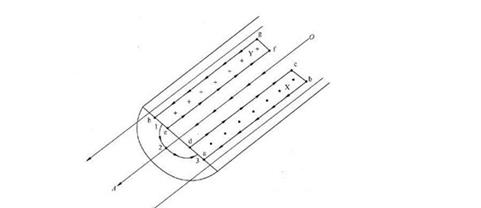
Skin effect: also
known as skin effect, when AC passes through the conductor, the current will be
concentrated on the surface of the conductor. This phenomenon is called skin
effect. Why is there such a physical phenomenon? The reason is that when the
conductor flows through AC, the electromotive force opposite to the current
direction will be generated inside the conductor, which acts as a hindrance to
the current flow. It is called back electromotive force here. The center of the
conductor is larger than the flux linkage on the surface of the conductor, so
the back electromotive force generated at the center of the conductor is larger
than that near the surface of the conductor. If the back EMF is large, the
current will flow on the surface of the conductor with smaller back EMF, while
no current will pass through the center.
In summary, skin
effect is only for AC, and automotive audio power supply uses 12 volts of
direct current, so its conductor, that is, power line, has no skin effect.
Therefore, pure oxygen-free copper is the best choice for automotive audio
power supply, but copper-clad aluminum is not suitable.
Skin effect sketch
of conductor
Successful
Solution: 0.1 Conductor Enameled Wire Multi-Core Structure:
AC cables will use the litz lacqued in the existing specification (conductor to each other use in solated with lacquer)
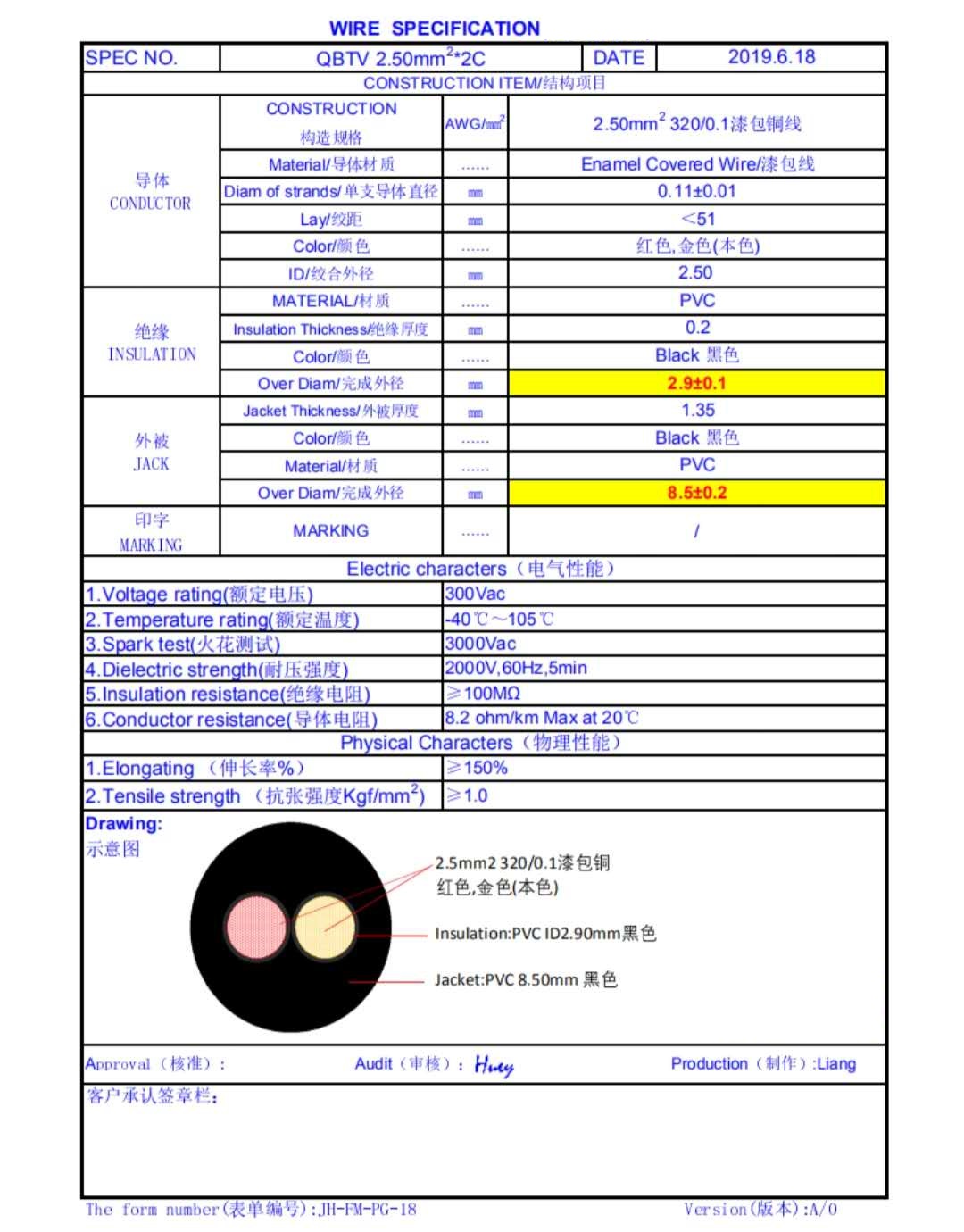
One way to alleviate the skin effect is to use the so-called Leeds line (from German: Litzendraht, meaning "woven thread"). The Leeds line uses the method of winding multiple metal wires to make the electromagnetic field more evenly distributed, so that the current distribution on each wire will be more evenly distributed. With Leeds line, the frequency of significant skin effect can be increased from thousands of hertz to several megahertz. Leeds line is generally used in high frequency AC transmission, which can alleviate skin effect and proximity effect at the same time.
